Advanced Composite Materials in Aerospace & Automotive
The aerospace and automotive industries are constantly pushing the boundaries of performance, safety, and efficiency. Advanced composite materials are playing a key role in achieving these goals.
In this article, we’ll delve into the exciting world of advanced composite materials and their applications in the aerospace and automotive industries.
What are Composite Materials?
Advanced composite materials are materials made from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties, that when combined, produce a material with characteristics different from the individual components.
They’re used in a variety of industries, including aerospace, automotive, and marine, due to their high strength, stiffness, and lightweight properties. Advanced composite materials can be designed to have specific properties, making them ideal for applications that require unique material performance characteristics.
The Role of Advanced Composite Materials in Aerospace and Automotive Applications
One of the most common types of composite materials used in aerospace and automotive applications is carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP). CFRP is a composite material made up of carbon fibers and a polymer resin. It is incredibly strong, lightweight, and durable.
When it comes to aerospace, CFRP has found its way into various components like aircraft fuselages, wings, and tail sections, and has enabled manufacturers to reduce weight and increase fuel efficiency compared to traditional materials such as aluminum.
Similarly, in the automotive industry, CFRP is now being used in body panels, chassis components, and wheels to replace heavier materials like steel. This results in weight reduction, better fuel efficiency, and improved handling and performance, making it a popular choice for manufacturers.
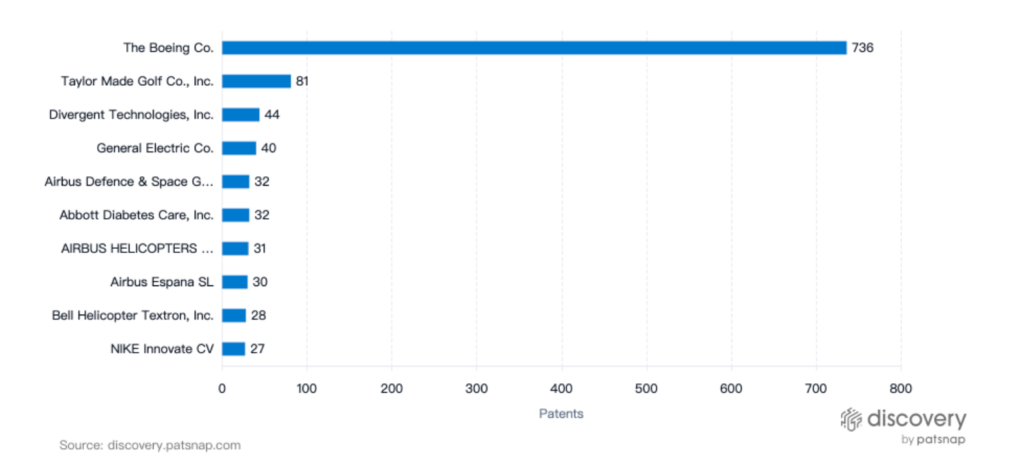
Boeing is the clear leader in the CFRP space, with an impressive 736 patents filed. This robust patent portfolio sets it apart from other filers in the space and demonstrates the company’s significant investment in this technology. It’s safe to say that Boeing has a stronghold on the CFRP industry and is driving innovation in this field.
Ultimately, the versatility and benefits of CFRP make it a promising material for both industries, leading to further exploration and development of its potential uses.
Other Advanced Composite Materials Used in Aerospace and Automotive Applications
In addition to CFRP, there are a number of other advanced composite materials being used in aerospace and automotive applications. These include fiberglass reinforced polymer (FRP), aramid fiber reinforced polymer (AFRP), and hybrid composites.
FRP is similar to CFRP, but is made up of fiberglass rather than carbon fibers. It is less expensive than CFRP, but still offers many of the same performance advantages.
AFRP is a composite material made up of aramid fibers and a polymer resin. It is incredibly strong and lightweight, and is often used in ballistic protection and other high-performance applications.
Hybrid composites are made up of two or more different types of fibers, combined to create a material that has superior performance characteristics. For example, a hybrid composite might be made up of carbon fibers and aramid fibers, combining the strength and stiffness of carbon fibers with the impact resistance of aramid fibers.
The Advantages of Tailoring Composite Materials to Specific Applications
By customizing the type and proportion of fibers, as well as the type of polymer resin used, composite materials can be designed to have specific performance characteristics, such as increased strength, stiffness, or impact resistance. For instance, in the aerospace industry, carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites (CFRP) are used to manufacture aircraft structures because of their high strength-to-weight ratio. On the other hand, glass fiber reinforced polymer composites (GFRP) are commonly used in wind turbine blades due to their high stiffness-to-weight ratio, making them capable of withstanding high wind loads.
Furthermore, advanced composite materials can also be customized to meet specific requirements for temperature, moisture, and chemical exposure. For instance, aramid fibers such as Kevlar can be used to create composites that have high resistance to heat, while carbon fibers are used to create composites that have excellent resistance to corrosive chemicals. This ability to tailor composite materials to specific applications results in superior performance, increased durability, and ultimately, reduced costs over the lifespan of the product.
As new composite materials are developed and existing materials are refined, we can expect to see even more breakthroughs in the years to come.